Checking the need for control action
If the convergence criteria of the InvControl are satisfied, no control action is sent to the control list in the current iteration, j. However, for the first control iteration, j = 1, always the action is sent, so the criteria given below are only valid for j > 1.
Voltage convergence criteria The voltage criterion is performed by comparing the monitored voltage in pu between the control iterations j and j − 1, according to Equation 41.

If the DRC function is selected, the Equation 42 presents the convergence criterion that needs to be satisfied.
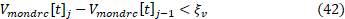
Where ξv corresponds to the tolerance defined in the VoltageChangeTolerance property.
If the combined volt-var and DRC function is enabled, both the criterion of Equation 41 and Equation 42 must be satisfied.
Reactive power convergence criterion The convergence criterion for reactive power is performed by comparing the desired reactive power in pu, qDend[t]j, and the reactive power in pu of the controlled element, both from the control iteration j, as Equation 43.


Where:
- ξq corresponds to the tolerance defined in the VarChangeTolerance property;
- qDend[t]j is discussed in the Equation 75 of Step 4;
- Qbase[t]j−1 and Qbaseneg [t]j−1 are the base reactive power values for the provided and absorbed reactive powers from the previous control iteration, j 1, respectively. The calculation of these values is presented in Step 4.
Active power convergence criterion The convergence criterion for active power is per- formed by comparing the active power limit in pu, pLend[t]j, with the active power limit in pu which is the result of the convergence process, according to Equation 45.
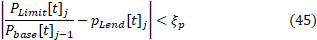
Where:
- ξp corresponds to the tolerance defined in the ActivePChangeTolerance property;
- pLend[t]j is discussed in the Equation 74 of Step 4;
- Pbase[t]j−1 is the base active power value from the previous control iteration, j 1. The calculation of these values is presented in Step 4.
It is important to notice that this comparison does not use the output active value of the controlled element. The reason is that the nature of the volt-watt function is to set an active power limit instead of a desired value. Therefore, the convergence criterion for active power could be satisfied with an output active power of the controlled element less than the active power limit set by the volt-watt function.
Step 3: Control Actions for t Done? The control loop converges for a time step t when there is no control action in the control list for this time step. Otherwise, the process proceeds to Step 4 described below.
Step 4: Execute Control Actions for t The control action for InvControl is performed by changing the reactive power and/or limiting the active power of the PVSystem. The items performed in this step are described here.
