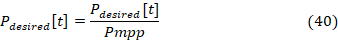Calculation of the per-unit monitored voltage
The monitored voltage in pu, vmon[t]j, applied to the smart inverter volt-var and volt-watt functions, is calculated using the monitored voltage in V , Vmon[t]j, through one of the options in the voltage_curvex_ref property shown below:
– For rated, the monitored voltage in pu is calculated according to Equation 33.

– For avg, the monitored voltage in pu is calculated according to Equation 34.
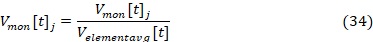
– For ravg, the monitored voltage in pu is calculated according to Equation 35.

Where:
– Vmonavg [t] is the mean value of the monitored voltages in pu of the previous m time steps that can be stored in the moving window with length defined in the avgwindowlen property, as can be seen in Equation 36.
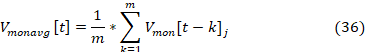
For instance, an averaging window with three time step length, Vmonavg [t] is calculated according to Equation 37.
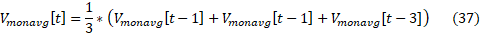
For smart inverter DRC functions, the monitored voltage in pu is always calculated according to Equation 38.

- Calculation of the output active power desired in pu The smart inverter functions watt- pf and watt-var do not depend on any voltage to operate, instead they just need the output active power desired. The output active power desired is the power that the inverter would provide or absorb if kVA rating of the inverter is not exceed. For the PVSystem, it is calculated as shown in the Equation 39.

Where:
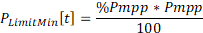
The base active power value used for those functions is the rated active power in which for the PVSystem is the Pmpp, according to the Equation 40