Troubleshooting
Manual Registration of COM Server
If you do not intend to automate OpenDSS, and simply use the OpenDSS.EXE stand-alone version, you could skip this step and simply copy the EXE and DLL files to some convenient location on your disk. Afterward, you can manually register the server by issuing the following command to the (DOS) command prompt when in the folder you have placed the files:
Regsvr32 OpenDSSEngine.DLL
The RegisterDSSEngine.BAT file provided within the standard zip file download to perform this action. Registration need only be done once. You may simply double-click on the .BAT file and it will execute the registration.
Note: You may need Administrator privileges on your computer to do this. This applies more to Windows 10, 8, 7 and Vista than previous versions of Windows.
On Windows Vista, 7, 8, and 10 you will have to execute the .BAT file from an elevated Admin status. One way to do this is right click on the Windows buttonand select Command Prompt (Admin). Then run the .BAT file from the command window, or DOS window. Some corporate IT policies may require you to go through additional steps. It may be necessary to have an administrator install the intial copy of OpenDSS. Once installed, you can simply update by copying the newer EXE or DLL over the older one in most cases.
After registration, if you start the Windows registry editor (Type ‘regedit’ in the command box on the start menu) you will find the OpenDSSEngine listed under Classes, as shown below.
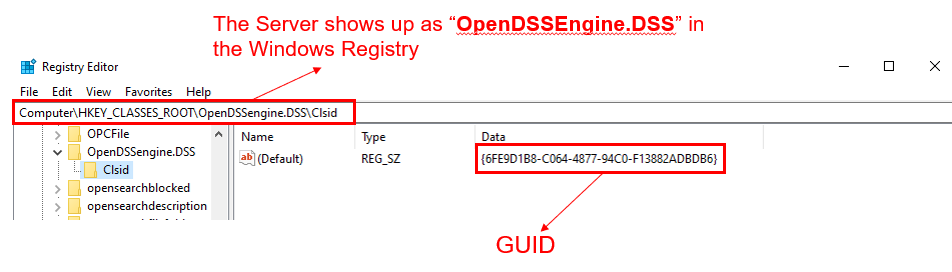
Figure 1. OpenDSSEngine in the Windows Registry
If you then look up the GUID in the registry, it should point to the OpenDSSEngine.DLL file in the folder where you installed it.
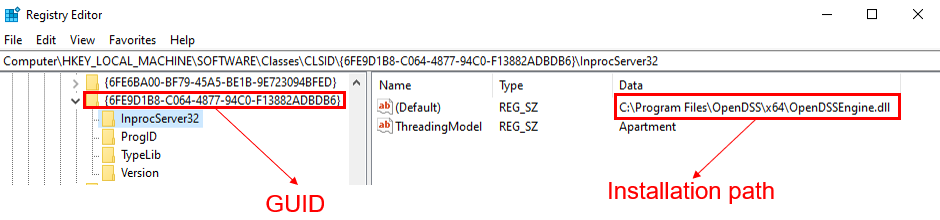
Figure 2. GUID points to the In-Process Server File (OpenDSSEngine.DLL)
The key shown is for the 64-bit version CLSID on Windows pointing to the server in the x64 folder. The full registry key is:
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\CLSID\{6FE9D1B8-C064-4877-94C0-F13882ADBDB6}
Note that on 64-Bit Windows systems, the 32-bit server version CLSID will be registered under the Wow6432Node key with a key like this:
HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\Wow6432Node\CLSID\{6FE9D1B8-C064-4877-94C0-F13882ADBDB6}
This is the registry key for the 32-bit “Windows on Windows” (WoW) part of the registry. This is how Windows knows which version of the server to load even though the GUIDs are the same.
Although there are many interfaces in the OpenDSS COM interface, only one is registered: the DSS interface. The program automatically instantiates the rest of the interfaces when it starts. Then you can define some variables in your program to the various interfaces to make it convenient to access the intefaces. For example, our common startup routine in Excel VBA is:
Public Sub StartDSS()
' Create a new instance of the DSS
Set DSSobj = New OpenDSSEngine.DSS
' Start the DSS
If Not DSSobj.Start(0) Then
MsgBox "DSS Failed to Start"
Else
' MsgBox "DSS Started successfully"
' Assign a variable to each of the interfaces for easier access
Set DSSText = DSSobj.Text
Set DSSCircuit = DSSobj.ActiveCircuit
Set DSSSolution = DSSCircuit.Solution
Set DSSControlQueue = DSSCircuit.CtrlQueue
Set DSSCktElement = DSSCircuit.ActiveCktElement
Set DSSPDElement = DSSCircuit.PDElements
Set DSSMeters = DSSCircuit.Meters
Set DSSBus = DSSCircuit.ActiveBus
Set DSSCmath = DSSobj.CmathLib
Set DSSParser = DSSobj.Parser
Set DSSIsources = DSSCircuit.ISources
Set DSSMonitors = DSSCircuit.Monitors
Set DSSLines = DSSCircuit.Lines
Range("DSSVersion").Value = "Version: " + DSSobj.Version
Beep
End If
End Sub
